Revolutionary Discovery of Self-Reproducing Skyrmions for Data Storage
Written on
Chapter 1: Introduction to Skyrmions
Recent advancements in data storage technology have captured the attention of researchers. A notable breakthrough, referred to as ‘DORIS,’ has emerged, offering a promising approach to enhance DNA data storage, making it more dynamic and scalable.
Researchers at the Ames Laboratory, part of the U.S. Department of Energy, have made a groundbreaking discovery of a subatomic quasiparticle known as a skyrmion. This unique particle mimics biological cells by possessing the ability to replicate itself, yet it lacks mass, acting like a subatomic entity in various respects.
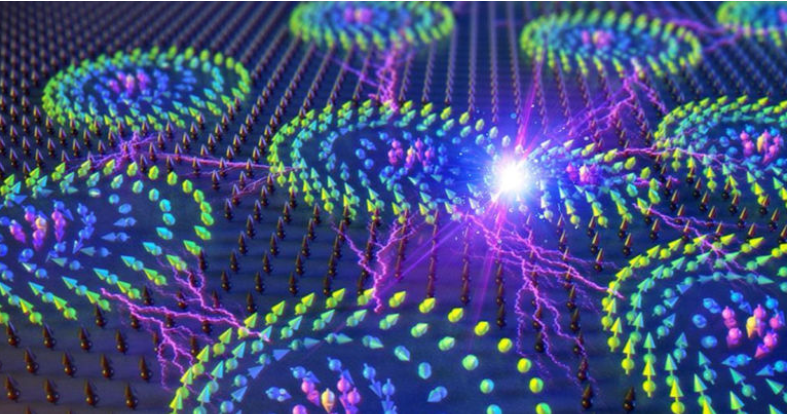
Chapter 1.1: Understanding Skyrmion Formation
"In order to integrate skyrmions into future devices, science must have an accurate understanding of their formation mechanism. In this research, we directly proved that skyrmion crystal grows from a conical magnetic phase in the same way as real nanocrystals grow from solution."
~ Lin Zhou, Lead Researcher
Skyrmions consist of energy and magnetic forces that organize into arrangements akin to the structured atoms found in crystals. Researchers believe that by manipulating these subatomic entities, significant advancements in data storage and transfer technologies could be achieved.

Section 1.2: Mechanism of Self-Replication
The researchers have demonstrated that skyrmion crystals grow from a conical magnetic state in a manner similar to how nanocrystals form from a liquid solution. Remarkably, skyrmions can rectify imperfections in their lattice structure through self-replication, akin to biological cell reproduction. This self-healing process is unprecedented in scientific literature.
Scientists utilized micromagnetic simulations alongside a string method to delve into the growth mechanisms of skyrmions and investigate the interactions and transition pathways among different spin states. Lead researcher Lin Zhou suggests that this understanding could enhance the control and manipulation of skyrmions, potentially leading to the creation of high-density, energy-efficient data storage and transfer devices.
The video titled "Scientists create tiny living robots from human cells | WION - YouTube" explores cutting-edge advancements in the field of bioengineering, highlighting how these innovations relate to the discovery of skyrmions.
Chapter 2: Conclusion and Future Implications
The complete findings of this research have been published in the Journal Nano Letters, marking a significant milestone in the quest for next-generation data storage solutions.

Stay informed with the content that matters — Join my mailing list