Monero (XMR): A Comprehensive Overview of Privacy-Focused Crypto
Written on
Chapter 1: Introduction to Monero
Today, we are excited to delve into the world of Monero (XMR), a cryptocurrency that has gained significant traction.

Overview The cryptocurrency landscape is continually evolving, with new innovations emerging regularly. Bitcoin's supremacy faces challenges from various digital currencies, including Monero. This currency has quickly positioned itself in the market due to its use in controversial transactions, such as those related to the black market and online drug trade. However, it's important to clarify that Monero is not illegal; it is widely appreciated for facilitating anonymous transactions.
Monero stands out as a premier cryptocurrency dedicated to providing private and censorship-resistant transactions. Unlike many existing cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum, which operate on transparent blockchains allowing for tracking and verification of transactions, Monero employs advanced privacy measures to protect its users' identities.
Monero was initially launched in April 2014 under the name BitMonero, a combination of "Bit" (inspired by Bitcoin) and "Monero," which means "coin" in Esperanto. Shortly after its inception, the name was shortened to Monero. It originated as the first fork of Bytecoin, with notable differences such as:
- A reduction in block generation time from 120 seconds to 60 seconds.
- A cut in the issuance rate by 50%, which was later adjusted back to 120 seconds while maintaining the issuance schedule by doubling the block reward for each new block.

The Controversy Surrounding Monero In recent years, Monero has faced scrutiny due to its association with illicit activities. For instance, in 2018, hackers who stole approximately 500 million NEM tokens from Coincheck found it challenging to exchange those tokens for Monero. This cryptocurrency has gained notoriety for its connections to ransomware, scams, and organized crime on the dark web. However, labeling Monero as a scam would be inaccurate; it remains one of the largest cryptocurrencies globally, with a significant market capitalization.
Monero's transactions are characterized by confidentiality and anonymity. Unlike selective alternatives like Zcash, Monero is designed to keep its users anonymous by default. The identities of the sender, receiver, and the transaction amount are concealed through three key technologies: stealth addresses, ring signatures, and RingCT. This inherent privacy means that Monero transactions cannot be traced, making it a truly fungible currency. Merchants and users who accept Monero can transact without the fear of blacklisting or token devaluation.
Monero has the potential to empower individuals to conduct transactions almost instantaneously without needing approval from any authority. This feature can be particularly advantageous in oppressive regimes, serving as a powerful instrument for freedom.
Chapter 2: The Monero Project and Its Innovations
This video provides an in-depth review of Monero, highlighting why it deserves your attention. Discover its features and market position.
The Monero Project is at the forefront of advancing privacy and security in the cryptocurrency realm. Its dedicated Research Lab and Development Team consistently innovate, with contributions from over 500 developers worldwide since its launch.
Monero is essentially a fully anonymous cryptocurrency, adhering to the fundamental principles of blockchain technology. Historically, even law enforcement agencies have struggled to trace the identities of senders and recipients in Monero transactions, underscoring its potential as a robust privacy-focused currency. Many users are on the lookout for completely anonymous tokens for secure transactions, making Monero appealing to this demographic.
Mining Monero Mining is a crucial term in the cryptocurrency ecosystem, referring to the digital process of validating transactions and earning rewards. It is not merely the creation of money but a complex verification procedure utilizing computing power.

Mining serves as a mechanism for validating transactions within a cryptocurrency network. A miner—be it an individual or organization—contributes processing power to receive a portion of the same cryptocurrency as compensation. This process helps lower transaction fees and incentivizes miners to support the network.
I have previously covered cryptocurrency mining in another video. If you missed it, here’s the link!
In this video, we explore the essentials of cryptocurrency mining and its significance in the digital currency landscape.
Monero operates on a proof-of-work mining model to achieve consensus across its distributed network. The Monero Project does not endorse specific mining pools, software, or hardware. Mining is vital for network security, and Monero utilizes RandomX, an ASIC-resistant algorithm designed to keep mining accessible to regular consumer-grade hardware.
Future Developments for Monero As Monero approaches its seventh anniversary, it has implemented several changes and advancements. Let’s take a look at its roadmap for 2021 and beyond.
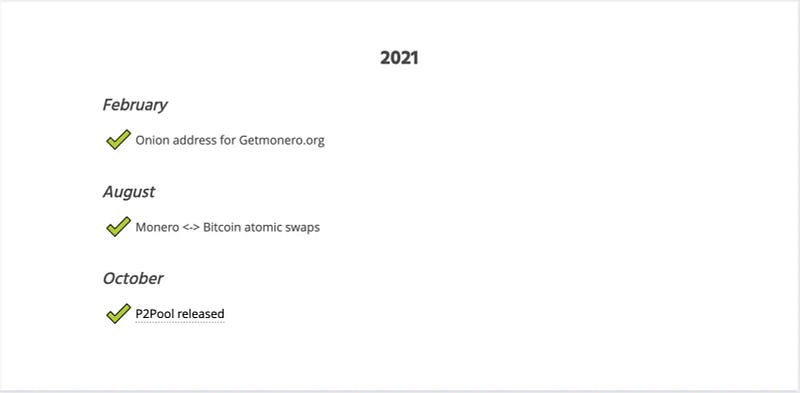
Looking Ahead

Through this exploration of XMR, we have uncovered valuable insights into Monero's mining processes and its future ambitions! Are you currently engaged in mining this cryptocurrency? Next week, I will introduce another exciting cryptocurrency, so make sure to follow my profile to stay updated on my upcoming articles on Medium!
See you soon!
New to trading? Consider exploring crypto trading bots or copy trading options.