The Major Deception in Contemporary Physics
Written on
Chapter 1: The Rise of Jan Hendrik Schön
At the dawn of the 21st century, experimental physics experienced a remarkable advancement, primarily due to Jan Hendrik Schön's contributions. This German physicist, who was affiliated with Bell Labs—the birthplace of the transistor—was considered a true genius. His experiments appeared to propel physics into a new era.

Schön conducted innovative experiments that seemed to dramatically advance the field of physics. His prolific output of research papers was the envy of many esteemed scientists, with Schön managing to publish an astonishing one article every eight days at one stage in his career. His works appeared in top-tier journals like Nature and Science, with nearly 100 articles published within a few years.
One of Schön's most significant claims was the development of a molecular-level transistor made from organic materials. This breakthrough promised to revolutionize electronics, enabling a higher density of transistors in integrated circuits and significantly reducing production costs. A new era of powerful and affordable computing technology seemed imminent!
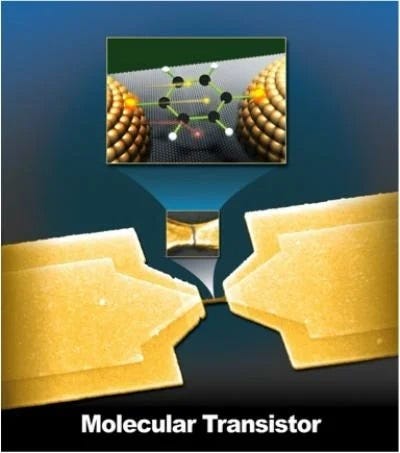
Chapter 2: The Unraveling of a Legend
Schön quickly ascended to fame, captivating audiences at scientific conferences where anticipation for his presentations reached a fever pitch. His achievements were almost too remarkable to be true.
However, it soon became evident that other researchers struggled to replicate Schön's results. It became clear that his findings only seemed valid under his supervision, which contradicts the core principle of scientific inquiry: replicability. One researcher noted that two data tables from different experiments in Schön's papers exhibited identical noise levels, a statistically improbable occurrence. As scrutiny intensified, the facade of Schön’s discoveries began to crumble.
The first video titled "Eugenie Reich: Plastic Fantastic: How The Biggest Fraud In Physics Shook The Scientific World" delves into the ramifications of Schön's actions and how they impacted the scientific community.
Investigations revealed that Schön had manipulated results to secure additional funding from Bell Labs, driven by a desire for fame and recognition.

When called upon to provide comprehensive raw data from his experiments, Schön claimed to have "deleted" it to clear space on his hard drive. An internal inquiry at Bell Labs uncovered substantial evidence that at least 18 of his 24 reported experiments had been falsified.
Thus, the elaborate structure Schön had built came crashing down. His publications were retracted, he lost his position, and all scientific accolades were revoked, including his Ph.D.

To my knowledge, Schön has never publicly admitted to his misconduct or offered a coherent explanation for his actions. Nevertheless, this scandal highlighted significant flaws in the scientific peer review process of the time.
The second video, "Overhyped Physicists: Richard Feynman," provides additional context on the expectations placed upon physicists and the potential for deception within the field.
In the aftermath of this incident, it became evident that reviewers and scientific peers must not only evaluate the originality and merit of research papers but also actively seek out potential falsifications and fraudulent practices. What could have been a monumental breakthrough in materials physics and electronics turned out to be a significant deception.
If you want to read more articles about space, feel free to clap! Subscribe to our channel for answers to your questions in future articles. If you appreciate my work, consider supporting me by becoming a Medium member for just $5 a month, which will help us produce even better content.